
The technology sector is currently navigating a period of significant transformation, marked by widespread workforce adjustments. As artificial intelligence (AI) continues its rapid advancement, its role in these changes—and specifically in recent layoffs—has become a central topic of discussion. This article delves into the recent wave of layoffs in major tech firms, examines the multifaceted role of AI, identifies the departments most affected, explores the human impact, and looks toward the future of tech employment.
Key Insights: Understanding the AI and Layoff Nexus
- AI's Complex Role: Artificial intelligence is a significant catalyst in recent tech layoffs, primarily through automation and efficiency gains, but it often acts in concert with broader economic pressures, corporate restructuring efforts, and strategic business pivots.
- Widespread Impact and Emerging Opportunities: While roles involving routine and data-intensive tasks (e.g., in software engineering, customer support, and HR) are most susceptible to AI-driven changes, the technology is simultaneously paving the way for new job categories, particularly in AI development, ethics, and oversight.
- The Human Element is Critical: Successfully navigating this transition necessitates a profound focus on supporting the affected workforce through comprehensive reskilling and upskilling initiatives, robust mental health resources, and proactive adaptation strategies from both individuals and organizations.
A Tumultuous Period: Layoffs Across Tech Giants in 2024-2025
The years 2024 and 2025 have been characterized by substantial job cuts across the tech industry. Major companies, including Microsoft, Meta (formerly Facebook), Google, and Amazon, have announced significant workforce reductions. For instance, Microsoft initiated layoffs affecting approximately 6,000 employees in May 2025, which amounted to about 3% of its global workforce, with impacts notably felt in software engineering and management layers. Google also undertook restructuring, leading to hundreds of job cuts in divisions like HR and cloud services in early 2025. Meta continued its "year of efficiency" ethos with further role eliminations after substantial cuts in 2023, aiming to reallocate resources towards AI development.
Overall, the scale has been considerable. Data indicates that tens of thousands of tech workers faced layoffs in 2024, with some reports suggesting figures exceeding 140,000 globally within the tech sector by mid-2024. This trend persisted into 2025, with thousands more roles eliminated in the first half of the year. These figures underscore a sector-wide recalibration as companies adapt to new technological paradigms and economic realities.

The Multifaceted Role of AI in Workforce Reductions
Artificial intelligence is undeniably a significant factor influencing these layoffs, but it's rarely the sole cause. Instead, AI often acts as an accelerator or enabler for broader strategic decisions.
Automation and Efficiency
AI's capacity to automate routine and repetitive tasks is a key driver. Companies are leveraging AI to enhance productivity and streamline operations. This can lead to a reduced need for human intervention in certain roles. For example, AI-powered tools can now handle aspects of coding, data analysis, customer service inquiries, and administrative tasks more efficiently than ever before.
Restructuring and Strategic Pivots
Many tech companies are undergoing significant restructuring efforts to align with new strategic priorities, particularly focusing on AI development and integration. This "renewed focus on AI" is often cited as a reason for reallocating resources, which can involve phasing out roles deemed less critical to future growth while aggressively hiring for AI-specific talent. CEO statements often frame these changes as necessary for long-term competitiveness and innovation. For instance, Microsoft's CEO Satya Nadella, while acknowledging AI's role in boosting efficiency, also linked layoffs to reducing management layers and strategic realignments. Similarly, Google's Sundar Pichai mentioned cuts as a way to "drive velocity" in key AI priority areas.
Economic Factors and CEO Perspectives
Economic headwinds, such as inflation, higher interest rates, and concerns about a potential recession, also contribute to cost-cutting measures, including layoffs. Some argue that tech companies overhired during the pandemic-driven boom and are now correcting their headcount. The CEO of Klarna, Sebastian Siemiatkowski, openly stated that AI helped the company shrink its workforce by approximately 40%, alongside factors like natural attrition, highlighting how AI investments can directly correlate with workforce reductions in specific contexts. However, many companies are cautious about explicitly linking layoffs solely to AI, possibly to mitigate employee anxiety and public backlash.
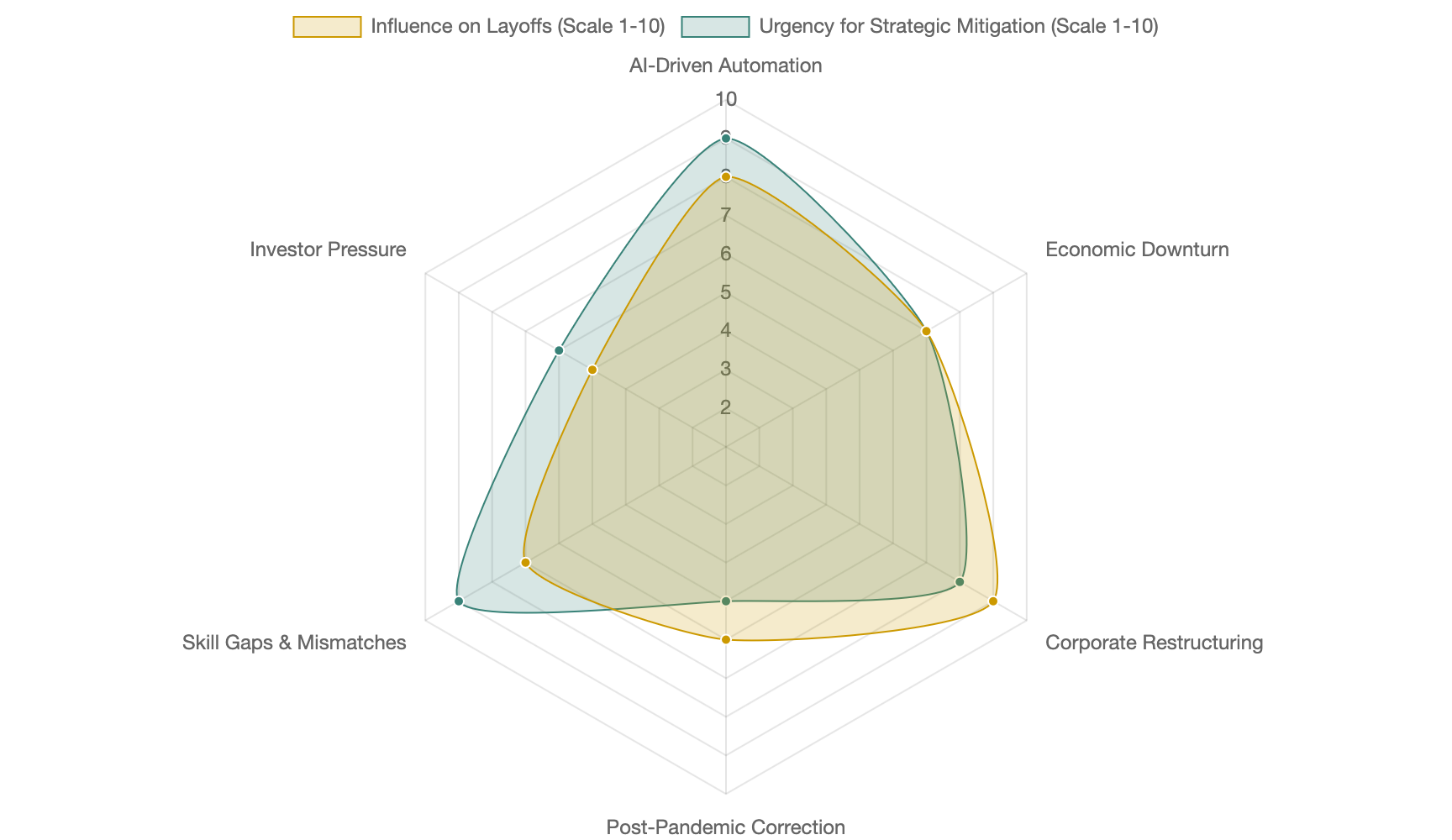
Visualizing the Drivers: Factors Influencing Tech Layoffs
The recent wave of tech layoffs is not a monolithic event driven by a single cause. Instead, it's a confluence of several interconnected factors. The radar chart below offers a visual representation of the perceived influence of various drivers behind these workforce adjustments in 2024-2025, as well as the urgency for strategic mitigation from an industry perspective. These are qualitative assessments based on prevailing industry analyses and expert opinions, designed to illustrate the complexity of the situation.
Impacted Departments and Roles: Where AI's Effect is Most Pronounced
The integration of AI is not uniformly affecting all job functions. Certain departments and roles are more susceptible to AI-driven automation and restructuring. The following table outlines some of the key areas experiencing significant changes:
| Department/Role | AI's Primary Impact | Examples of Affected Tasks | Notable Company Actions/Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Engineering & Development | Automation of routine coding, testing, and design tasks; Augmentation of developer productivity. | Code generation, bug detection, automated testing, UI/UX prototyping. | Microsoft's layoffs significantly impacted software engineers. Reports suggest AI can write substantial portions of code. |
| Customer Support & Services | Automation of query handling, support ticket resolution, and personalized customer interactions. | AI chatbots, virtual assistants, automated email responses, call routing. | Klarna reported workforce reduction partly due to AI handling customer service tasks. |
| Human Resources (HR) | Automation of recruitment processes, employee onboarding, payroll, and administrative HR tasks. | Resume screening, scheduling interviews, benefits administration, HR data analysis. | Google included HR roles in its restructuring and layoffs. |
| Legal Services | Automation of document review, legal research, contract drafting, and due diligence. | AI tools for e-discovery, case law analysis, compliance checks. | Increased adoption of AI legal tech tools like Harvey and CoCounsel. |
| Finance & Accounting | Automation of data entry, financial analysis, fraud detection, and algorithmic trading. | Transaction processing, report generation, risk assessment. | Predictions of significant job reductions on Wall Street in back and middle office roles. |
| Administrative & Middle Management | Automation of scheduling, data management, report generation, and other routine administrative tasks. | Calendar management, email organization, document preparation. | Reductions in entry-level and middle management roles as companies streamline operations. |
| Manufacturing | Automation of assembly line tasks, quality control, and supply chain optimization. | Robotic process automation, predictive maintenance, visual inspection. | MIT and Boston University report projected AI replacing up to two million manufacturing workers by 2025. |
It's important to note that in many cases, AI is augmenting human capabilities rather than causing outright replacement, leading to a transformation of job roles rather than complete elimination.
The Human Toll: Mental Health, Reskilling, and Job Loss
Beyond the statistics and corporate strategies, the wave of layoffs has a profound human impact. Job loss is often accompanied by financial instability, emotional distress, and uncertainty about the future.

Mental Health and Well-being
The anxiety surrounding job security in an AI-disrupted landscape is palpable. A Pew Research study found that a majority of U.S. workers (around 52%) express concern about AI's potential impact on their jobs. The stress of potential or actual job loss, coupled with the fear of skills becoming obsolete, can take a significant toll on mental health.
The Imperative of Reskilling and Upskilling
In this rapidly evolving environment, continuous learning, reskilling, and upskilling have become paramount. Many tech companies are investing in programs to help their workforce adapt. Amazon, for example, committed $1.2 billion to its "Upskilling 2025" initiative, aiming to retrain 300,000 employees for more technical roles. IBM's Justina Nixon-Saintil has emphasized that "learning does not just stop anymore," highlighting the need for a lifelong learning mindset. However, concerns remain, particularly regarding the shrinking number of entry-level positions as AI automates more routine tasks, potentially making it harder for new talent to enter the tech field.
Exploring the Narrative: AI and Job Displacement
The conversation around AI and its impact on employment is complex and often polarizing. The following video, "Tech Layoffs 2024: Is AI to Blame?", delves into some of these nuances, examining the relationship between technological advancement and workforce changes. It explores whether AI is the primary driver of recent layoffs or if other economic and strategic factors play a more dominant role, offering perspectives that can help contextualize the ongoing shifts in the tech industry.
A discussion on the role of AI in the context of tech layoffs in 2024.
What's Next? The Evolving Future of Tech Jobs
The future of tech employment is being actively shaped by AI, leading to both challenges and opportunities.
Transformation of Roles and Creation of New Ones
While some jobs may be displaced or significantly altered by AI, new roles are also emerging. The World Economic Forum (WEF) has projected that while automation (including AI) might displace around 85 million jobs globally by 2025, it could also create 97 million new roles. These new positions will likely be concentrated in areas such as AI development, data science, AI ethics and governance, AI system maintenance, and roles that require uniquely human skills like complex problem-solving, creativity, and emotional intelligence.
Rising Demand for AI Skills and Retraining Efforts
There is a clear and growing demand for AI-related skills. Job postings requiring AI expertise have seen a steady increase. For instance, some data suggests AI-related job postings in the U.S. grew from 1.4% in 2023 to 1.8% in 2025. This creates a "mismatched talent market" where there's a pool of available IT professionals but a shortage of those with specific, in-demand AI skills. Consequently, robust retraining and upskilling initiatives are crucial. Governments and organizations worldwide are launching programs to address this, such as the European Commission's "Union of Skills" plan, aimed at future-proofing education and training systems.
Union Responses and Worker Advocacy
As AI's impact on the workforce becomes more pronounced, labor unions and employee advocacy groups are becoming increasingly vocal. They are calling for greater transparency from companies regarding their AI adoption plans, demanding better severance packages and protections for displaced workers, and advocating for ethical guidelines in the deployment of AI in workforce management. These groups play a vital role in ensuring that the transition is managed equitably and that workers' rights are upheld.
Conclusion: Embracing Change with a Balanced and Empathetic Outlook
The tech layoffs witnessed in 2024 and 2025 are a stark reminder of the dynamic nature of the industry. Artificial intelligence is a powerful force driving efficiency, innovation, and restructuring, but it operates within a complex ecosystem of economic pressures and strategic corporate decisions. While AI contributes to job displacement in certain areas, particularly those involving repetitive tasks, it also heralds an era of new opportunities and demands new skill sets.
Navigating this changing landscape requires a multifaceted approach. For individuals, it means embracing lifelong learning and adaptability. For companies, it involves responsible AI implementation, investing in their workforce through reskilling programs, and providing support for those affected by transitions. For society as a whole, it calls for thoughtful policies that balance technological advancement with social equity and worker well-being. A balanced outlook, one that acknowledges both the disruptive potential and the transformative benefits of AI, coupled with empathy for the human impact, will be crucial in shaping a future where technology and humanity can thrive together.
Recommended Further Exploration
- How can tech professionals future-proof their careers against AI disruption?
- What new job roles are emerging due to advancements in artificial intelligence?
- What ethical considerations should companies prioritize when implementing AI-driven workforce changes?
- Explore the global economic impact of AI on employment trends beyond the tech sector.
References
- Microsoft Layoffs Highlight AI-Driven Hiring Pauses
- Klarna CEO says AI helped company shrink workforce by 40%
- These Jobs Will Fall First As AI Takes Over The Workplace
- Is AI closing the door on entry-level job opportunities?
- What Jobs Will AI Replace?
- AI Jobs in 2025: Essential Insights for Software Engineers
- Tech Layoffs: US Companies With Job Cuts In 2024 And 2025